Written:
Feb 7, 2026
deBridge distributes 96% of all protocol fees to DBR stakers, roughly $800K per month. Learn how the zero-exploit bridge's tokenomics create real yield.
deBridge has quietly built one of DeFi's most compelling tokenomics models. While most cross-chain bridges struggle with token utility and value capture, the DBR token offers stakers a direct claim on 96% of protocol fees. With over $18 billion transferred, zero exploits, and roughly $10 million in annualized fees, deBridge tokenomics combine security, performance, and genuine yield in a market where most bridge tokens fail to deliver.
This guide examines how deBridge tokenomics work, what makes DBR valuable, and why the protocol's approach to fee distribution stands out in the cross-chain infrastructure landscape.
What is deBridge?
deBridge is a high-performance cross-chain bridge and interoperability protocol that enables secure asset transfers and messaging across 26+ blockchain networks. Unlike traditional bridges that rely on liquidity pools or wrapped tokens, deBridge uses an intent-based architecture called DLN (deSwap Liquidity Network) that provides instant transfers with zero slippage.
The protocol operates through a decentralized network of validators who stake DBR tokens to secure cross-chain transactions. This validator network uses multi-proof verification to confirm transaction validity, creating economic security through slashing mechanisms.
Since launching, deBridge has processed over $18 billion in cross-chain value with zero security exploits. The protocol supports transfers between major networks including Ethereum, Solana, Arbitrum, Base, and 22 other chains. Average transfer time is roughly 2 seconds, with fees typically ranging from $0.70 to $2.60 depending on network conditions.
The DBR Token: Core Functions
DBR serves as the native governance and utility token for the deBridge protocol, with a fixed maximum supply of 10 billion tokens. The token's design centers on three primary functions that align stakeholder incentives with protocol security and growth.
Network Security Through Staking
Validators must stake tokens to operate nodes and validate cross-chain transactions. This staking requirement creates economic security because validators risk losing their stake through slashing if they validate fraudulent transactions or fail to maintain infrastructure uptime. Delegators can also stake tokens with validators to share in validation rewards without running infrastructure themselves.
The slashing mechanism keeps validators honest and highly available. Any validator caught attempting double-spending, validating non-existent transactions, or experiencing excessive downtime faces stake penalties. This security model places financial responsibility directly on those who verify cross-chain transfers.
Governance Rights
DBR holders gain voting power over key protocol parameters through decentralized governance. Starting in Q1 2026, the protocol plans to transition full governance control to token holders, allowing them to determine validator elections, treasury management, new chain integrations, and fee structures.
This governance transition represents a shift from foundation-controlled decision-making to community-driven protocol evolution. Token holders will be able to propose and vote on protocol upgrades, validator set changes, and treasury allocations through on-chain voting mechanisms.
Fee Discounts and Revenue Distribution
DBR stakers receive reduced fees on cross-chain transactions, lowering the cost of using deBridge for transfers and swaps. More significantly, stakers earn a share of protocol revenue through the fee distribution mechanism, making deBridge token revenue directly tied to usage.
The protocol collects fees from every cross-chain transfer and swap. These fees are then distributed to validators and their delegators based on their stake weight and validation performance. This creates direct cash flow from protocol usage to token holders who secure the network, making deBridge token revenue a function of real demand.
deBridge Tokenomics: Distribution and Vesting
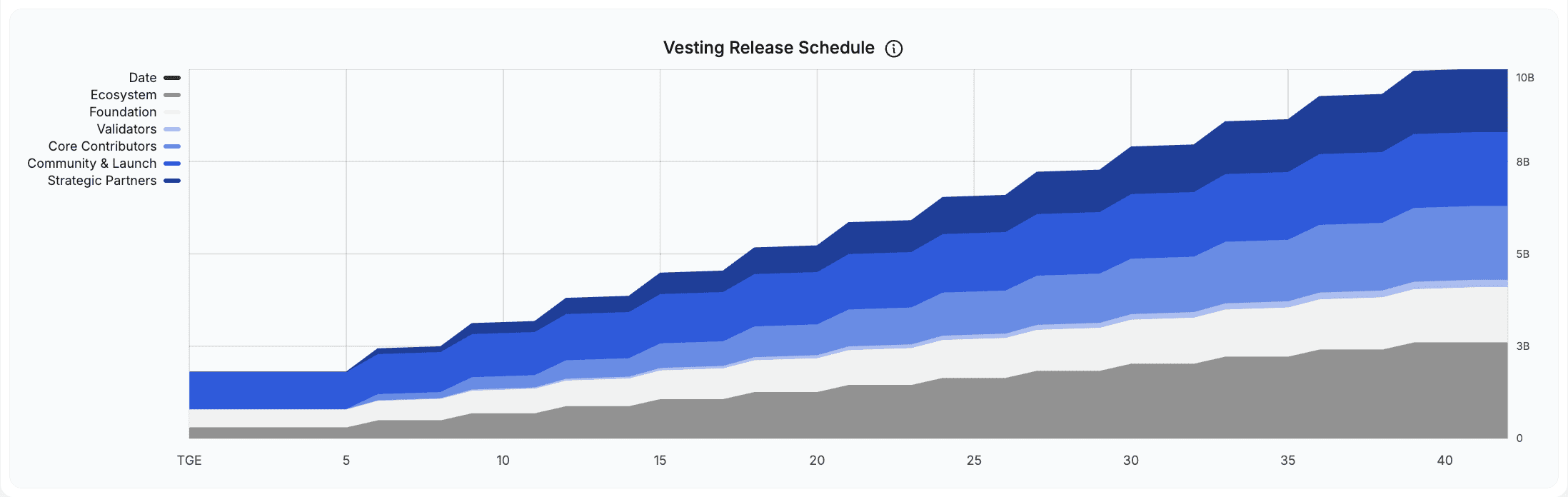
The 10 billion DBR total supply is allocated across six categories designed to balance community distribution, ecosystem growth, and long-term sustainability. The allocation structure and vesting schedules create a gradual supply release extending through 2028.
Token Allocation Breakdown
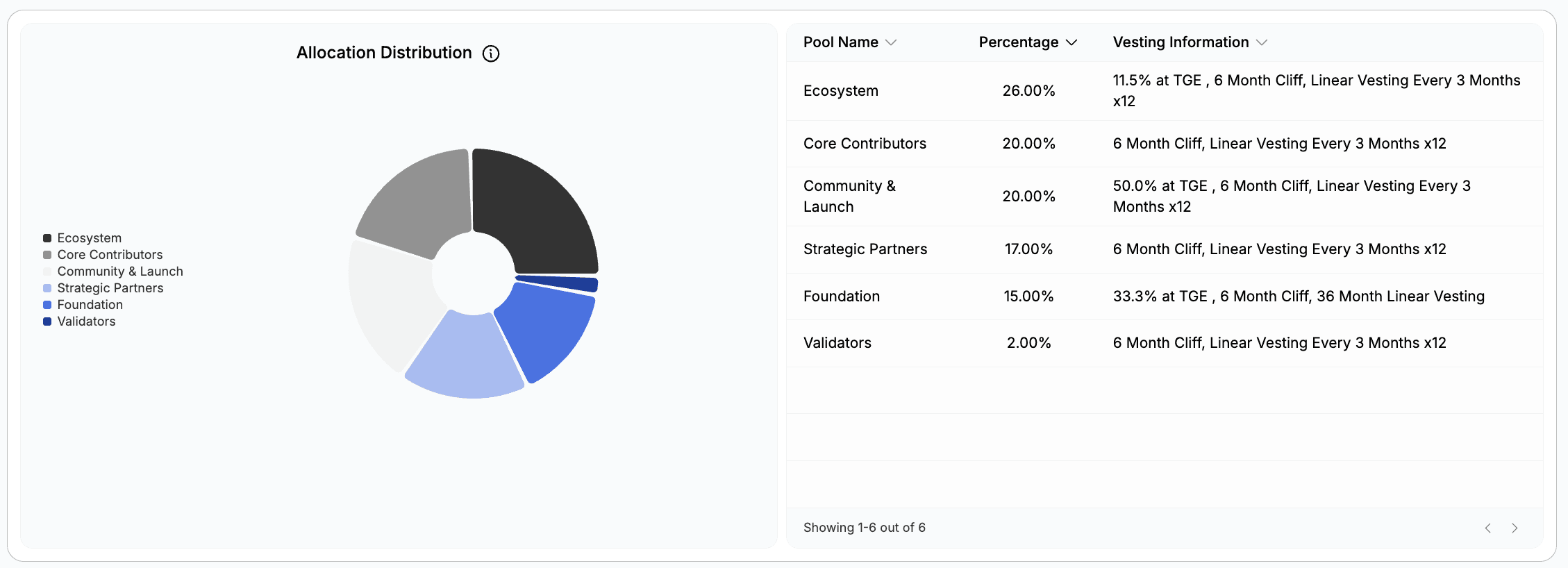
Category | Allocation | DBR Amount | TGE Unlock | Vesting |
Community & Launch | 20% | 2 billion | 10% | Quarterly, 3 years |
Ecosystem | 26% | 2.6 billion | 3% | Quarterly, 3 years |
Core Contributors | 20% | 2 billion | 0% | 6-month cliff, 3 years |
Strategic Partners | 17% | 1.7 billion | 0% | 6-month cliff, 3 years |
deBridge Foundation | 15% | 1.5 billion | 5% | Quarterly, 3 years |
Validators | 2% | 200 million | 0% | Quarterly, 3 years |
Community & Launch (20%, 2 billion DBR): Distributed through airdrops, points campaigns, and community rewards. This allocation incentivizes early users and active participants. At the Token Generation Event (TGE), 10% unlocked immediately, with the remaining 90% vesting quarterly over three years.
Ecosystem (26%, 2.6 billion DBR): Reserved for ecosystem development, developer grants, partnerships, and community engagement programs. This is the largest allocation, reflecting the protocol's focus on building cross-chain infrastructure. Only 3% unlocked at TGE, with the remainder vesting quarterly over three years to fund long-term growth initiatives.
Core Contributors (20%, 2 billion DBR): Allocated to team members who built and maintain the protocol. Zero tokens unlocked at TGE, with a six-month cliff before the first 4% unlocks. The remainder vests over three years, aligning team incentives with long-term protocol success.
Strategic Partners (17%, 1.7 billion DBR): Distributed to early investors and strategic partners who provided funding and support. No TGE unlock. After a six-month cliff, 3.4% of total supply (340 million DBR) unlocks, followed by quarterly vesting over three years.
deBridge Foundation (15%, 1.5 billion DBR): Supports the foundation's operations, research, and protocol development. 5% unlocked at TGE for operational needs, with the rest vesting quarterly over three years.
Validators (2%, 200 million DBR): Allocated to validator rewards for securing the network. This relatively small allocation is supplemented by ongoing fee revenue from protocol operations. Vests quarterly over three years.
deBridge Value Accrual: The 96% Fee Model
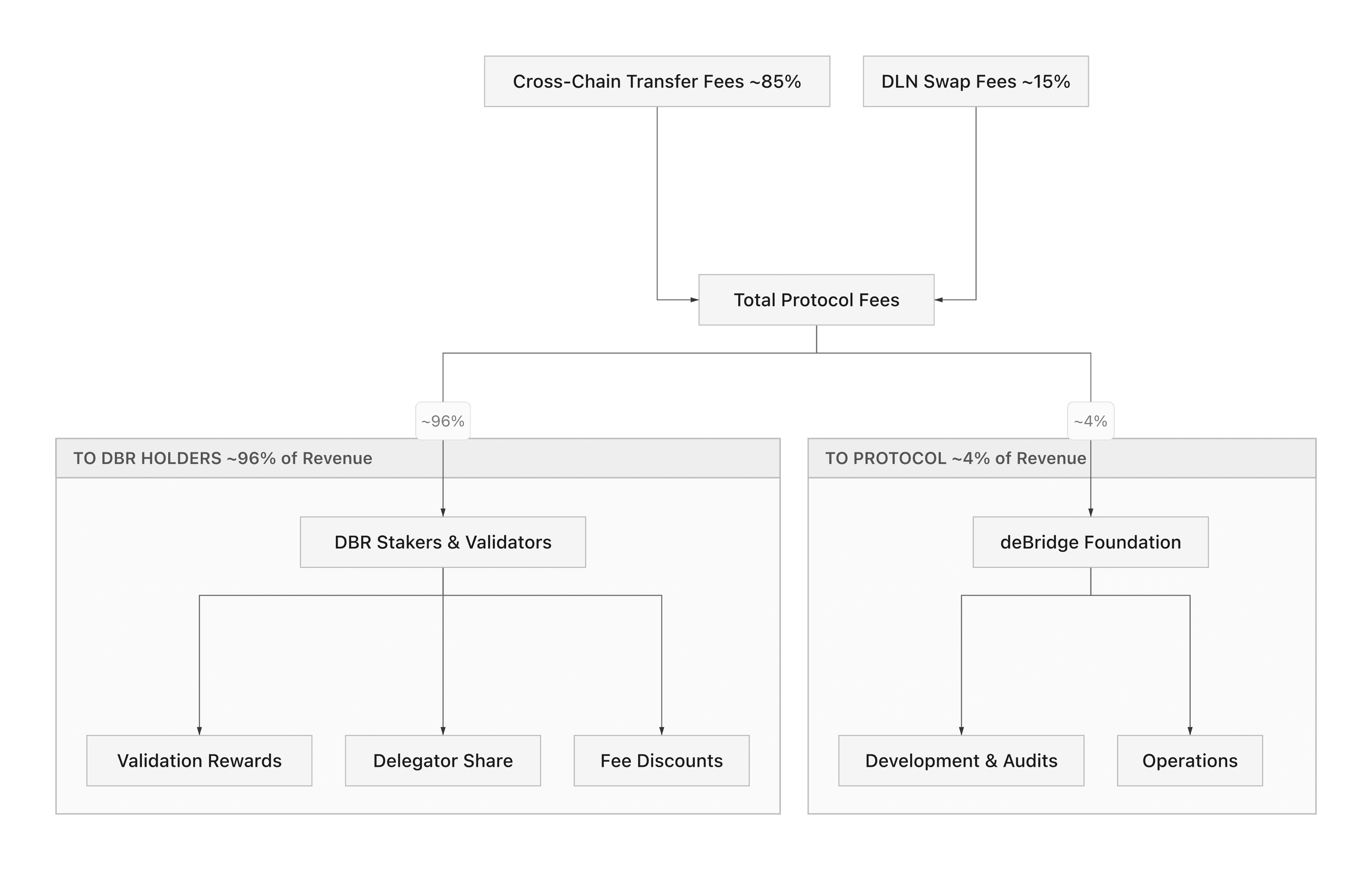
The standout feature of the deBridge protocol is its fee distribution model. Unlike most bridge protocols that retain the majority of fees in a treasury or burn tokens, deBridge routes 96% of all cross-chain bridge fees directly to DBR stakers and validators.
Fee Flow Breakdown
When a user sends a cross-chain transfer through deBridge, the protocol collects a small fee. That fee splits as follows:
96% to stakers and validators: Distributed proportionally based on stake weight and validation performance
4% to the deBridge Foundation: Funds ongoing development, audits, and operational costs
With approximately $10 million in annualized cross-chain bridge fees, this translates to roughly $800K per month flowing to DBR stakers. As bridge volume grows, so does the revenue pool, creating a direct link between protocol adoption and staker returns.
Why This Model Stands Out
Most bridge tokens offer only governance rights or speculative value. The DBR value accrual model is different because it ties token holding to real cash flow. Stakers who lock DBR earn a proportional share of actual protocol revenue, not inflationary emissions or token rebases.
This structure resembles a dividend model. If deBridge processes more volume, protocol fees grow, and stakers earn more. The 96% pass-through rate is among the highest in DeFi, giving DBR holders a stronger claim on protocol economics than most comparable tokens.
Comparing deBridge Staking Yield
DBR staking yield depends on total fees generated and the amount of DBR staked. At current volumes, estimated yields range from 5% to 12% APR depending on validator performance and delegation size. These yields come entirely from organic protocol usage, not from inflation or liquidity mining programs.
This fee-driven approach to staking means the yield is sustainable as long as bridge volume persists. It avoids the common problem of high initial APRs that collapse as emissions dry up.
Key Takeaways
deBridge tokenomics distribute 96% of protocol fees to DBR stakers and validators, one of the highest pass-through rates in DeFi.
DBR has a fixed 10 billion supply allocated across community (20%), ecosystem (26%), contributors (20%), strategic partners (17%), foundation (15%), and validators (2%).
deBridge has processed $18B+ with zero exploits, giving the protocol a strong security track record in a sector plagued by hacks.
deBridge staking yields come from real fees, not inflation, making returns sustainable as long as bridge volume holds.
DBR value accrual is directly tied to usage: more transfers mean higher fee revenue and more returns for stakers.
The deBridge fee distribution model represents one of the clearest examples of value accrual in the cross-chain bridge sector. By routing 96% of protocol fees to DBR stakers, the model creates a direct financial link between network usage and token holder returns. The combination of zero exploits, $18 billion in processed volume, and a fee-driven yield structure gives DBR a fundamentally different profile than most bridge tokens.
For anyone evaluating cross-chain infrastructure, understanding deBridge tokenomics is a strong starting point. The protocol's approach to fee distribution, validator security, and gradual supply unlocks offers a template that other projects may follow as the industry matures.
deBridge Tokenomics FAQ
About the Author
Founder of Tokenomics.com
With over 750 tokenomics models audited and a dataset of 2,500+ projects, we’ve developed the most structured and data-backed framework for tokenomics analysis in the industry.
Previously managing partner at a web3 venture fund (exit in 2021).
Since then, Andres has personally advised 80+ projects across DeFi, DePIN, RWA, and infrastructure.

