Written:
Feb 2, 2026
THORChain enables native cross-chain swaps without bridges or wrapped tokens. While most decentralized exchanges rely on wrapped assets or centralized...
THORChain enables native cross-chain swaps without bridges or wrapped tokens. While most decentralized exchanges rely on wrapped assets or centralized intermediaries, THORChain allows users to swap Bitcoin for Ethereum directly. At the heart of this system is RUNE, the network's native token that serves as the settlement layer for all liquidity pools and secures the network through node bonding.
RUNE holders capture value through multiple mechanisms. Liquidity providers earn swap fees, node operators earn block rewards and transaction fees, and the protocol burns a portion of all fees collected. With $902,000 in monthly holder revenue and $73 million distributed all-time, THORChain demonstrates how tokenomics can align incentives across liquidity providers, node operators, and long-term holders while maintaining decentralized cross-chain infrastructure.
What is THORChain?
THORChain is a decentralized liquidity protocol that enables cross-chain cryptocurrency swaps without wrapped or pegged assets. Built on the Cosmos SDK, the protocol supports Bitcoin, Ethereum, Binance Chain, Dogecoin, Litecoin, Avalanche, Bitcoin Cash, and Cosmos Hub, with plans to add Solana, Tron, Cardano, TON, and Base by 2026.
Unlike traditional bridges that create synthetic representations of assets, THORChain uses a network of independent nodes and continuous liquidity pools to facilitate direct swaps between native Layer 1 coins. When a user wants to swap BTC for ETH, they send Bitcoin to a THORChain vault address. The network observes this transaction, validates it through consensus, and automatically sends the equivalent value in Ethereum from its ETH liquidity pool to the user's destination address.
This architecture eliminates wrapped token risk while maintaining the speed and efficiency of automated market maker designs. THORChain processed $4.66 billion in swap volume during the week of March 2, 2025, following the Bybit hack, demonstrating the protocol's capacity during high-demand periods.
RUNE Token Distribution and Supply
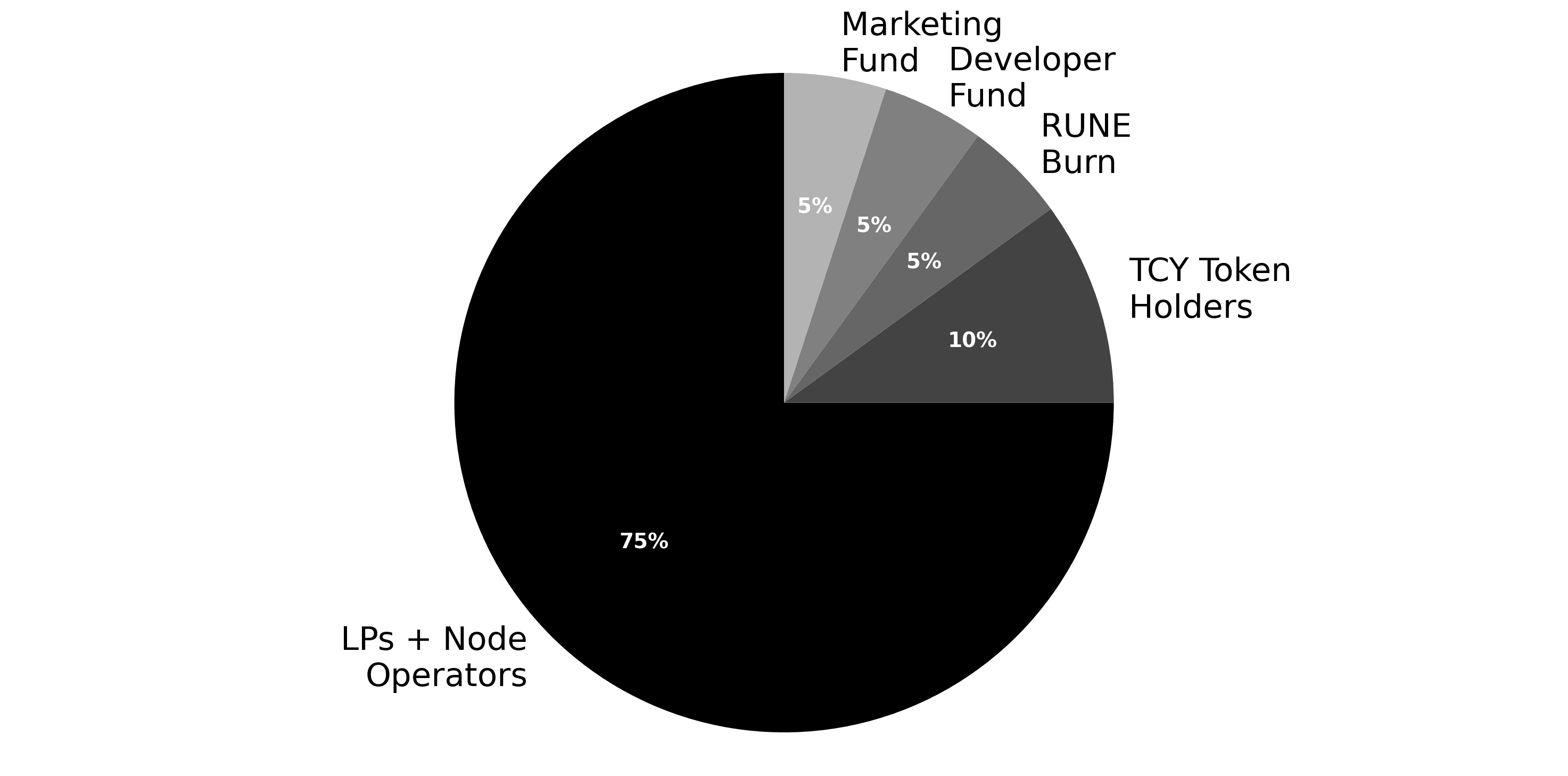
RUNE launched with a maximum supply of 500 million tokens. The initial distribution allocated tokens across multiple stakeholder groups to bootstrap liquidity, incentivize node operators, and fund protocol development.
The protocol implements a deflationary supply model by burning 5% of all swap fees collected. At current burn rates of approximately 1,200 RUNE per day, this mechanism gradually reduces circulating supply. Combined with the requirement for node operators to bond RUNE and liquidity providers to pair assets with RUNE, the token maintains consistent demand from network participants.
Token emissions follow a deterministic schedule based on block rewards. Node operators receive RUNE for validating transactions and maintaining network security. As the protocol matures and swap fee revenue grows, block rewards represent a smaller percentage of total node operator income, shifting the economic model toward fee-driven sustainability.
The distribution structure ensures that active network participants who provide liquidity or operate nodes accumulate the majority of RUNE over time. Passive holders receive indirect value accrual through supply burns and demand from pool requirements, but direct revenue flows to those actively securing or providing liquidity to the network.
THORChain Value Accrual: How RUNE Captures Revenue
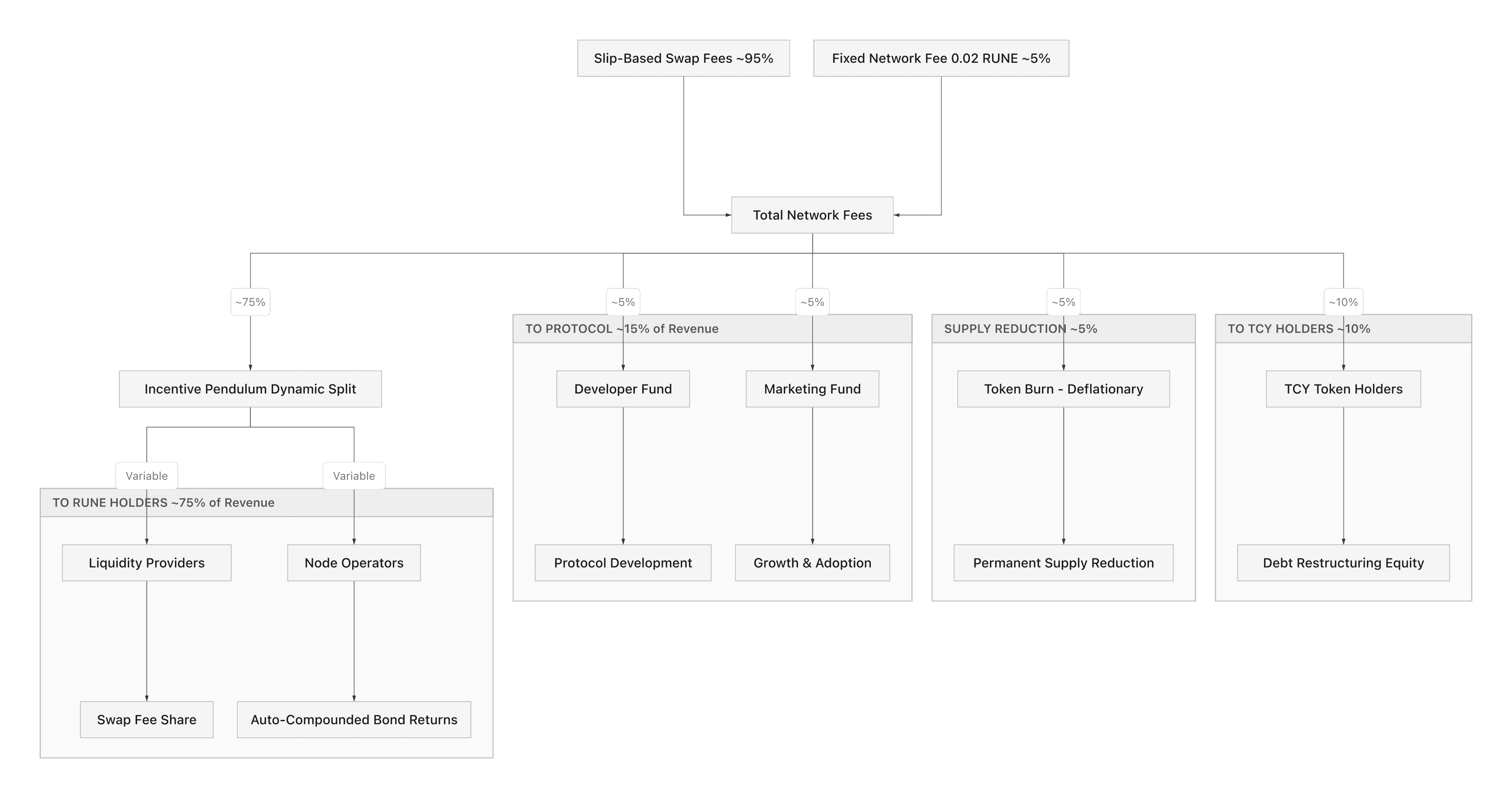
RUNE value accrual occurs through four primary mechanisms: required liquidity pool pairing, node operator bonding, fee accumulation, and supply burns. Each mechanism creates consistent token demand while distributing revenue to network participants.
Liquidity Pool Structure
Every asset on THORChain pairs with RUNE in a 1:1 value ratio. If a liquidity pool contains $100,000 worth of Bitcoin, it must also contain $100,000 worth of RUNE. This requirement makes RUNE the settlement layer for all cross-chain swaps.
When users add liquidity to THORChain, they must provide equal value in RUNE and the paired asset. This constant demand pressure comes directly from protocol mechanics rather than speculation. As total value locked increases, proportional RUNE value must be locked in pools.
Liquidity providers earn their share of swap fees proportional to their pool ownership. THORChain distributed $902,000 to holders in the most recent month, representing returns on both RUNE and paired assets. The 1:1 pairing requirement means liquidity providers face impermanent loss when RUNE's price diverges significantly from paired assets, creating a trade-off between fee income and value preservation.
Node Operator Bonding
THORChain's security model requires node operators to bond twice as much RUNE as exists in all liquidity pools combined. For every $1 of non-RUNE assets in pools, there is $1 of RUNE in pools and $2 of RUNE bonded by validators.
This 2:1 bond-to-pool ratio creates hard economic security. Node operators have more value at stake than the assets they secure, aligning their incentives with network safety. If a node operator attempts to steal assets or acts maliciously, they lose their bond, which exceeds the value they could potentially steal.
Node operators earn rewards relative to their bond size. The more RUNE a node operator bonds, the more block rewards and swap fees they earn, up to the effective bond cap. This mechanism incentivizes node operators to increase their bonds over time, raising the network's security budget as total value locked grows.
Nodes are rotated through a churning process approximately every 2.5 days. During churning, node rewards are distributed and new nodes can enter the active set if their bond exceeds that of the lowest-bonded active node. This competitive dynamic ensures the most committed node operators secure the network.
Fee Structure and Revenue Distribution
THORChain generates revenue from swap fees, outbound transaction fees, and affiliate fees. Swap fees vary dynamically based on the depth of liquidity pools and the size of trades. Larger trades relative to pool size incur higher slippage and fees, protecting liquidity providers from adverse selection.
Of all fees collected, 5% are permanently burned, reducing RUNE supply. The remaining 95% split between liquidity providers and node operators based on the Incentive Pendulum mechanism.
The Incentive Pendulum balances security and liquidity. If node bonds exceed optimal levels relative to pooled assets, the protocol directs more rewards to liquidity providers, incentivizing additional deposits. If bonds fall below optimal levels, more rewards flow to node operators, encouraging increased bonding.
This self-balancing mechanism maintains the 2:1 bond-to-pool ratio without manual governance interventions. Over time, it automatically adjusts reward distribution to ensure both adequate security and sufficient liquidity for efficient swaps.
THORChain captured 40.5% of $2.2 million in total protocol fees during recent measurement periods, directing $902,000 to token holders. This represents the portion of fees that flow to liquidity providers and node operators after the 5% burn.
Cross-Chain Swap Mechanics
THORChain executes cross-chain swaps through a three-stage process: observation, consensus, and execution. Understanding this flow clarifies how the protocol maintains security without centralized intermediaries.
When a user initiates a swap, they send their source asset to a THORChain vault address controlled by the active validator set through threshold signature schemes. Multiple independent nodes observe this incoming transaction on its native blockchain. Once the transaction receives sufficient confirmations, nodes report the observation to THORChain's state machine.
The THORChain network achieves consensus on the observed transaction through Tendermint BFT consensus. Once 67% of validators agree on the transaction details, the network updates its internal state to reflect the user's deposit. The state machine calculates the output amount based on the continuous liquidity pool formula, accounting for slip-based fees and price impact.
Finally, the network instructs its vault signers to execute the outbound transaction on the destination blockchain. The same threshold signature scheme that secured the incoming vault controls the outgoing transaction. The user receives their destination asset at their specified address on the target chain.
This entire process occurs without wrapping or synthetic assets. The Bitcoin sent by the user remains Bitcoin throughout the swap, held temporarily in THORChain's Bitcoin vault. The Ethereum received by the user is native ETH from THORChain's Ethereum vault, not a wrapped or pegged derivative.
The security of this system depends entirely on the economic value bonded by node operators exceeding the value they could steal from vaults. The 2:1 bond-to-pool requirement ensures this security assumption holds as long as RUNE maintains value and node operators act rationally.
Protocol Performance and Recent Developments
THORChain's financial performance reflects both the strengths of its core swap functionality and challenges from experimental features. Total value locked finished Q1 2025 at $181.1 million, down 50.5% from $368.6 million in Q4 2024. The decline resulted primarily from RUNE's 74.5% price correction during the same period.
Despite lower TVL, swap volume remained strong. The protocol processed $10.4 billion in swap volume during Q2 2025, representing a 71% year-over-year increase. This growth demonstrates strong product-market fit for native cross-chain swaps even as broader market conditions pressured token prices.
Fee revenue followed swap volume trends. THORChain generated over $6 million in swap fees during Q2 2025, distributing $902,000 to holders in the most recent measured month. Since inception, the protocol has distributed $73 million in cumulative holder revenue through liquidity provider fees and node operator rewards.
The protocol faced significant challenges in early 2025 when its THORFi lending program became insolvent due to unfavorable RUNE price performance. The program's systematic failure forced a full unwind, impacting liquidity providers who participated in lending markets. This event underscored the risks of expanding beyond core competencies, though THORChain's swap functionality continued operating normally throughout the crisis.
Following the lending program's closure, THORChain refocused on expanding its core cross-chain swap offering. Development priorities shifted toward integrating additional blockchains including Solana, Tron, Cardano, TON, and Base. The protocol also plans to launch Orbital Pools in August 2025, enabling expanded cross-chain liquidity through its App Layer.
An IBC connection with the broader Cosmos ecosystem is scheduled for 2026, potentially providing THORChain access to the liquidity and assets across dozens of Cosmos-based chains. Combined with plans to add thousands of additional tokens by Q1 2026, these integrations could significantly expand the addressable market for THORChain's swap infrastructure.
The deflationary supply mechanism continues reducing RUNE circulation. At current burn rates of approximately 1,200 RUNE per day, the protocol removes roughly 438,000 RUNE annually from supply. This deflationary pressure provides indirect value to holders, though the effect depends on burn rates remaining consistent or growing with swap volume.
Token Holder Considerations
RUNE holders face distinct risk-reward profiles depending on how they deploy their tokens. Passive holders gain exposure to deflationary supply dynamics and potential price appreciation from increased protocol usage, but receive no direct cash flows. Active participants who provide liquidity or operate nodes earn direct revenue at the cost of additional risks.
Liquidity providers earn their proportional share of swap fees from their pool. Returns vary based on swap volume through the pool, the depth of liquidity, and impermanent loss dynamics. When RUNE's price moves significantly relative to paired assets, liquidity providers experience impermanent loss that can exceed fee income.
The protocol's requirement for equal-value RUNE pairing means liquidity providers must maintain balanced exposure to both RUNE and their chosen paired asset. This forced diversification protects against total loss from any single asset but prevents concentrated exposure to assets with strong conviction.
Node operators face different considerations. Operating a THORChain node requires technical expertise, infrastructure investment, and significant RUNE bonding. The current competitive landscape means prospective node operators must bond more RUNE than the lowest-bonded active node, creating a rising capital requirement as the network matures.
Active node operators earn block rewards and swap fees proportional to their bond. These rewards can be substantial during high-volume periods but decrease during low-activity phases. Node operators also face slashing risks if their infrastructure fails or they attempt malicious behavior, potentially losing their entire bond.
The balance between these participation methods depends on individual risk tolerance, technical capability, and market outlook. Strong RUNE price appreciation benefits all holder categories, while price declines hit liquidity providers particularly hard through combined impermanent loss and asset depreciation.
Risks and Limitations
THORChain's tokenomics depend on several assumptions that may not hold under all market conditions. The most critical assumption is that RUNE maintains sufficient value for the 2:1 bond-to-pool ratio to provide meaningful security. If RUNE's price collapses while bonded amounts remain constant in token terms, the dollar-denominated security budget shrinks, potentially enabling economic attacks.
The protocol faced this scenario during early 2025 when RUNE's price declined 74.5% in one quarter. While node operators maintained their bonds, the declining RUNE price reduced the dollar value securing network vaults. The protocol remained secure during this period, but extreme price declines could theoretically reduce security below critical thresholds.
Impermanent loss represents a persistent challenge for liquidity providers. The requirement to pair assets 1:1 with RUNE means liquidity providers face impermanent loss whenever RUNE's price diverges from paired assets. During strong RUNE rallies, liquidity providers underperform simply holding RUNE. During RUNE declines, they face losses exceeding those from holding paired assets alone.
Competition from other cross-chain solutions poses ongoing risk to swap volumes and fee revenue. Centralized exchanges offer deeper liquidity and lower fees for most trading pairs. Layer 2 rollups and traditional bridges provide faster settlement for users who can tolerate wrapped asset risk. THORChain must maintain competitive pricing and user experience to sustain volume against these alternatives.
Regulatory uncertainty affects THORChain's long-term viability. The protocol's permissionless nature and lack of geographic restrictions could attract regulatory scrutiny in jurisdictions with strict cryptocurrency regulations. Node operators and liquidity providers may face legal questions about their roles in facilitating cross-chain transfers.
Smart contract risks remain present despite multiple audits. THORChain's architecture spans multiple blockchains and requires complex coordination between nodes, vaults, and state machines. Bugs in any component could result in locked funds, incorrect swaps, or security vulnerabilities. The protocol has experienced exploits in the past, though none have permanently compromised its core functionality.
The failed THORFi lending program demonstrates the risks of expanding beyond core competencies. While the swap functionality remained intact, the lending program's insolvency damaged confidence and forced liquidations. Future protocol expansions carry similar risks if they introduce complex dependencies or unforeseen failure modes.
Key Takeaways
RUNE serves as the settlement layer for all THORChain liquidity pools, requiring 1:1 value pairing with every supported asset.
Node operators must bond twice as much RUNE as exists in all pools combined, creating economic security through aligned incentives.
The protocol distributes $902,000 monthly to token holders through liquidity provider fees and node operator rewards, totaling $73 million all-time.
THORChain burns 5% of all swap fees, removing approximately 1,200 RUNE from circulation daily.
Native cross-chain swaps without wrapped tokens differentiate THORChain from bridge-based alternatives, eliminating wrapped asset risk while introducing dependence on node operator economic incentives.
Recent challenges with the THORFi lending program demonstrate expansion risks, though core swap functionality remains reliable with $10.4 billion in Q2 2025 volume.
Conclusion
THORChain demonstrates how tokenomics can create self-reinforcing incentives for decentralized infrastructure. RUNE's role as the required settlement asset and security bond creates consistent demand from protocol usage rather than speculation. The deflationary supply mechanism and fee distribution model reward active network participants who provide liquidity or operate nodes.
The protocol's value proposition rests on eliminating wrapped token risk while maintaining competitive swap pricing and user experience. As THORChain expands to additional blockchains and increases supported assets, maintaining the balance between security, liquidity, and decentralization will determine whether its tokenomics continue generating sustainable value for RUNE holders.
THORchain Tokenomics FAQ
About the Author
Founder of Tokenomics.com
With over 750 tokenomics models audited and a dataset of 2,500+ projects, we’ve developed the most structured and data-backed framework for tokenomics analysis in the industry.
Previously managing partner at a web3 venture fund (exit in 2021).
Since then, Andres has personally advised 80+ projects across DeFi, DePIN, RWA, and infrastructure.

